
Jump to:
Knowing when to use digital cutting versus die cutting is important because it can help you save time and money while producing the results you expect. Both die and digital cutting are excellent methods that offer customization possibilities and precise results. However, which cutting method is best for a given project depends on factors such as material, volume and design complexity.
American Micro Industries offers high-quality die cutting services you can count on for precise results and cost-effective solutions.
Advanced cutting solutions allow companies to produce components that fit their products and applications precisely. Industries such as the following use digital and die cutting for various purposes:
Die and digital cutting machines can perform the following cuts:
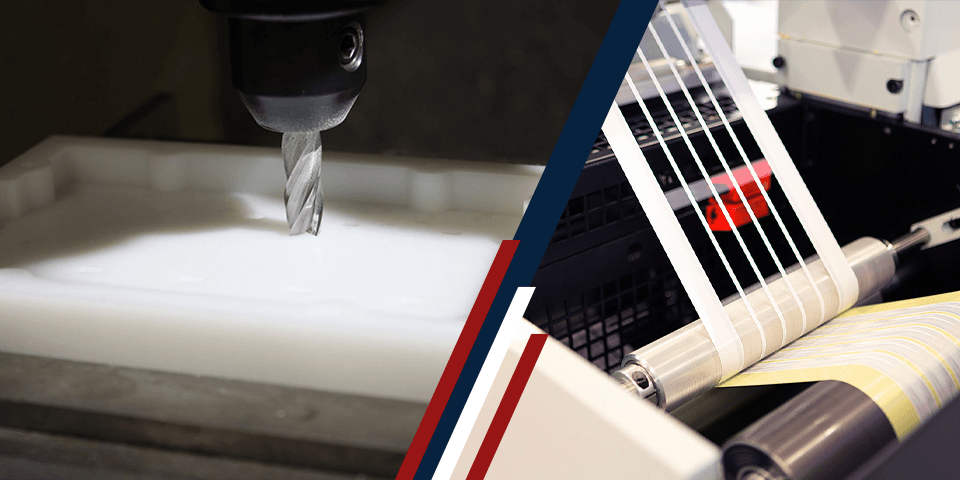
Die cutting is a process that cuts a thin material such as paper, fiberboard, acrylic or plastic to a specific size and shape. It’s a fast way to cut many printed items to uniform dimensions, and it has been a popular cutting method for numerous industries since its debut during the Industrial Revolution.
When you choose die cutting for your application, you purchase a custom-made punch block called a die that the cutting company creates based on your specific project design. To produce the die, a professional bends and folds a steel blade into your designed shape, then secures it to a sturdy block. This blade can then cut as many replicas of your original design as necessary.
Today, manufacturers like American Micro Industries use numerous die cutting techniques to accomplish specific goals. Though the blade construction varies, the basics of the process are consistent. A machine operator loads your custom blade into the machine, followed by the printed or blank material you wish to cut. Next, the machine presses the die and the material together, producing items in the shape of your die.
Digital cutting is a type of die-less precision cutting that involves a computer and a blade, laser or other type of cutting tool. A programmer will set tool paths according to the desired shape using the computer, then activate the machine to cut that shape into the material. With this technology, industries have more cutting possibilities.
During the digital cutting process, a machine operator feeds the material to be cut onto a flat table or conveyor. The machine’s arm moves milling, cutting, laser and scoring attachments forward, backward, right and left to follow the programmed tool path. This process produces the cuts, scores and creases your final material needs for your desired shape.
Both of these cutting techniques are highly effective, but their unique characteristics make each better suited for different applications. Consider these similarities and advantages of each if you’re trying to decide when to use digital cutting versus die cutting.
Die cutting machines are very precise, as a die’s blade creates a consistent finish and crisp, smooth edges. Since the process uses the same blade for each cut item, you can expect uniform results with little to no discrepancy.
Digital cutting offers exceptional cutting precision thanks to laser technology. Digital cutting machines use lasers and blade attachments to automatically follow programmed paths, resulting in clean edges.
Die cutting and digital cutting solutions can work for both small- and large-scale applications. However, the best method for your project depends on the size of the material you want to cut and the number of uniform items you need.
One of the advantages of die cutting over digital cutting is its high-volume capabilities and efficiency. With die cutting, you can produce a large volume of finished products at once, especially when using thin materials.
Large-format digital cutting is typically the best option if your design includes very intricate shapes or you need to produce a large graphic installation using thicker or tougher materials. It’s best for large-format printed elements such as retail signs or branding collateral. Digital cutting is also the best option for low-volume projects where you only need to cut a few items, as it allows you to cut the shape you need without investing in a custom die.
The method you should choose also depends on your project timeline. Digital cutting tends to have shorter initial turnaround times since it only requires the creation of tool paths, so it’s ideal when you need your products quickly. However, if you know you’ll be ordering the same product repeatedly and in larger quantities, investing in a die may be worthwhile. Plus, once the die is made, production is quick and simple.
Choosing the most cost-effective cutting method depends on your specific project material, volume and design intricacy.
Die cutting is a cost-effective option if you need to cut a large amount of thinner materials in the same shape. Since you can purchase one die and use it multiple times, you get more value from your purchase. Additionally, die cutting machines waste little material around the shapes they cut, making this process an excellent choice if you want a more environmentally friendly method.
Digital cutting is a more efficient and cost-effective option when you need to cut a limited number of items and don’t anticipate reruns in the future. However, it’s technically a slower process because the digital machine must follow a programmed cutting path for each item rather than simply stamping the design into the material in one step. It’s therefore inefficient for higher-volume orders and may be less cost-effective than die cutting at a certain point.
Die and digital cutting methods both offer a high degree of customizability.
Technicians can customize die blades to specific designs and project needs. For example, you may use die cutting to place creases in your packaging or create marketing materials shaped like your company’s logo to increase brand awareness. Die cutting machines can cut materials such as the following:
Digital cutting allows industries to cut a wide range of materials in various sizes and materials, and it can produce more intricate shapes if you have a complex design to cut.
A digital cutting machine can also handle thicker stock, allowing you to create larger, heavier or more durable finished products. Popular options include the following:
Operators can also integrate digital cutting machines with various software programs and printing machines, expanding their capabilities. For example, they can print your company’s logo on a large piece of material and then cut it to a specific shape for signage.
When choosing between die and digital cutting, it’s important to consider how much flexibility you need. Consider how intricate your design is and whether you may need to make changes throughout the process.
Die cutting is an excellent option if you are confident in your design and plan to continue using it for various purposes or future print runs. However, reforming a die is difficult and costly, so digital cutting may be the better option if you’re still workshopping your design.
Digital cutting offers much more design flexibility than die cutting when it comes to adjustments, as changing the output only requires updating the tool paths. While adjustments may incur additional costs, that amount will be considerably less than the cost of a new die.
A comparison of digital cutting versus die cutting reveals benefits to both methods. Determining which one is better depends on your unique project needs. Overall, die cutting is a better option if you need to cut a high volume of thinner materials. Digital cutting is typically the best option if you plan to make a low-volume order, have a complex design or need to cut thicker materials.
If you need assistance determining how to approach a specific design, the team at American Micro Industries is here for you. We can perform the following types of cutting services:
Die and digital cutting are both excellent material cutting methods, but choosing the right one for your application is essential for keeping your project on track and reducing overhead costs. American Micro Industries provides cost-effective die cutting and laser cutting services to businesses across various industries. From custom packaging products to precise electrical insulating components, we can provide high-quality parts for your needs.
Our expert team performs high-quality, in-house cutting, and our turnkey solutions equip you to complete projects and receive your cut components quickly. Contact us to learn more about our services and request a free quote.